

Much of the method development in the field of Multidisciplinary Design Optimization (MDO) attempts to simplify the design of a large, complex system, by dividing the system into a series of smaller, simpler, and coupled subsystems. This becomes ever more difficult as the complexity of the product increases. Industry is constantly pursuing faster and cheaper means for designing and manufacturing high quality goods and services. Using these queries on SCU simulation, we show that the SCU outperforms a software-only DSMS running on an AMD Opteron 2350 quad-core processor by 1.5-42 times. Finally, this paper presents the performance of SCU using four queries that represent common data stream processing use-cases, one of them being similar to a query found in the Linear Road Benchmark. In order to better explain the instruction set, design, and functionality of the various units in the SCU, this paper also provides a brief overview of SymQL-a procedural query language that we developed to describe the queries that can be executed on the SCU. To meet these requirements, the SCU exploits unique characteristics of DSMSs, such as single-pass tuple processing, windowed operators, and inherent data level parallelism, using a single-instruction multiple-data very large instruction word (SIMD-VLIW) microarchitecture and a novel inverted distributed register file. The SCU is intended for streaming applications with real-time event and data processing that have stricter deadlines, high-bandwidth, and high-accuracy requirements.
This paper describes the design and the architecture of symbiote coprocessor unit (SCU)-a programmable streaming coprocessor for a heterogeneous reconfigurable logic-assisted data stream management systems (DSMSs) such as symbiote. In a second article (entitled The Machine of the Mind, Part II − The role of synchronization in brain information processing), I will carry out a survey on the main anatomical and functional aspects of the mammalian brain, in order to describe the most interesting discoveries that have taken place during the past two decades of the last century and the perspectives that have opened up in understanding the processes that underlie the functioning of cognitive memory.
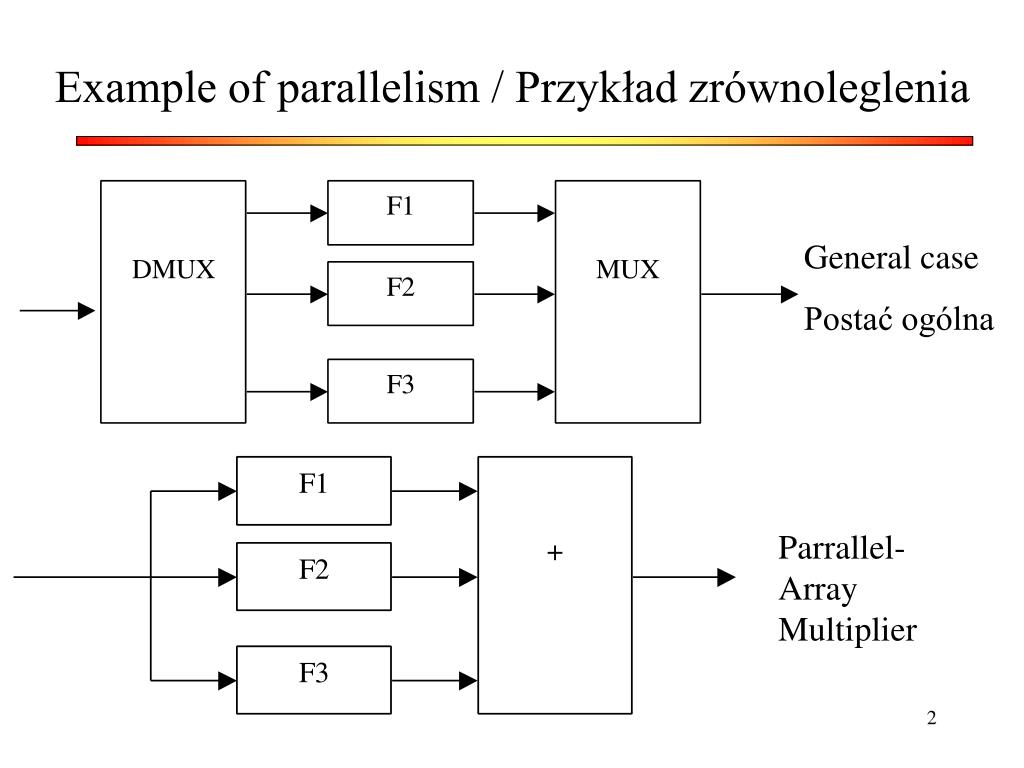
#Parallel processing serial#
Finally, I will compare the working principles of serial calculation with those of parallel calculation to try to understand if there are substantial differences of principle between the processing capacity of computers and those of animal brains. After a brief historical analysis of the Boolean logical paradigm, I will introduce some theoretical arguments which are essential for understanding how the self-reflexive capacity of human thought can be produced and I will try to explain the reasons that lead to consider the human brain as a universal recursive machine. In this paper I will deal with some topics concerning artificial intelligence. It is hoped that the present survey will help the proper application and interpretation of measurements. Depending on the network and the analysis task one has in mind, a specific set of features may be chosen.
Important related issues covered in this work comprise the representation of the evolution of complex networks in terms of trajectories in several measurement spaces, the analysis of the correlations between some of the most traditional measurements, perturbation analysis, as well as the use of multivariate statistics for feature selection and network classification. It includes general considerations about complex network characterization, a brief review of the principal models, and the presentation of the main existing measurements. This article presents a survey of such measurements. The analysis, discrimination, and synthesis of complex networks therefore rely on the use of measurements capable of expressing the most relevant topological features. Each complex network (or class of networks) presents specific topological features which characterize its connectivity and highly influence the dynamics of processes executed on the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
